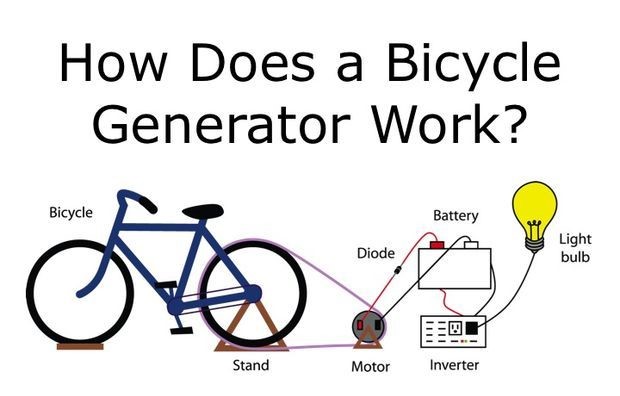
While there are undoubtedly limits to technology without electricity, its value ultimately relies on the situation and the needs at hand. Here are some things to think about:
-
- Realisticness Technology: Certain technologies can continue to work even in the absence of electricity, particularly those whose primary functions do not depend on it. For instance, non-electronic communication devices, basic mechanical tools, and agricultural implements can all still be useful under some circumstances.
- Resilience technology: Technology that can operate without energy might be immensely useful in places where it is either absent or inconsistent. This covers off-grid options such as solar-powered gadgets, hand-cranked radios, and hand tools that can be utilised in harsh or isolated settings.
- Historical and Cultural Technology Significance: There are historical and cultural implications to several non-electric technologies. Understanding and conserving these technologies can help us understand the inventiveness and lifestyles of the past.
- Education and Skill Development: Practical skills, resilience, and problem-solving abilities can all be enhanced by teaching and learning about technology that operates without power. It promotes innovation and resourcefulness in overcoming obstacles.
But it’s equally critical to recognise the limitations. Many contemporary technologies are very dependent on electricity to work, and they might not be viable or useful without it. Furthermore, electricity frequently makes it possible to use technology more conveniently and efficiently, which can greatly improve productivity and quality of life in a variety of situations.
Whether technology without electricity is worthwhile ultimately relies on the particular demands, conditions, and objectives of people or communities.

Without energy, is technology possible? That would be like inquiring about a wheel-less automobile! But first, let’s investigate. People continued to create and employ a variety of technologies even in the absence of widespread access to electricity. Here are few instances:
-
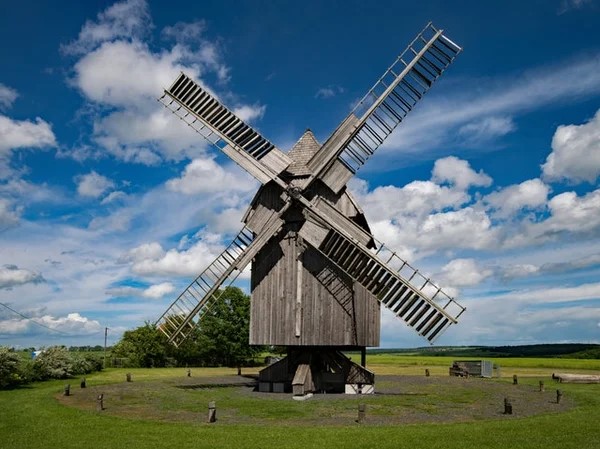
- Mechanical Technology: The concepts of gears, levers, and pulleys served as the foundation for numerous early technologies. Clocks, windmills, and watermills were examples of devices that ran without electricity and were powered by mechanical mechanics.
- Analogue Communication: Long before cellphones and the internet, humans used analogue technologies such as carrier pigeons, smoke signals, semaphore flags, and basic telegraph systems to communicate across great distances.
- Mechanical Transportation: Transportation was done by means of machines before the invention of electric trains and cars. Trains were propelled by steam engines, and horse-drawn carts and carriages were typical.
- Agricultural Tools: From irrigation systems to ploughs and scythes, agriculture has always been heavily reliant on technology. A large number of these tools were entirely mechanical and operated without the use of electricity.
- Traditional Crafts: Generation after generation has passed down artisanal skills and craftsmanship. Many traditional crafts, like weaving, pottery, and woodworking, require little to no electricity.
- Simple Medical Instruments: Long before the invention of contemporary electrical medical equipment, simple medical instruments such as forceps, scalpels, and stethoscopes were in use for centuries.
- Natural Energy Sources: Throughout history, people have used their muscles, the wind, and water as natural energy sources to complete activities. For example, grain was ground and water was pumped using windmills and waterwheels.
- Manual Labour: A lot of the jobs that are powered by electricity or automated now were formerly done by hand. Human labour was essential to getting things done, from grinding grain to cleaning clothes. These examples demonstrate how human intelligence and inventiveness have led to the invention of innumerable innovations that functioned quite well without electricity, despite the fact that electricity has revolutionized technology in many ways. Moreover the labour requires grapel stones to run on the base to produce electricity without conveying the problems. Atmost the covert labouers work immensely hard to wind the mill but not in the form of workforce but in the form of machines.